Arc Builder Learning Journal
November 4, 2025
The Next Internet Economy, Built on Arc with USDC

# Agentic Commerce
# autonomous agents
# Circle Wallets
# Dev-Controlled Wallets
# x402
# Hackathons
A Guide for Developers to Build the Agent Economy Using Circle’s Arc Stack

Blessing Adesiji

Imagine a near-future where digital workers aren’t human at all – they’re autonomous AI agents. Instead of clocking in each day, you deploy an AI agent online and let it handle real-world digital tasks for others. Every time your agent completes a job – whether it’s analyzing data, writing code, managing content, or executing an online service – it gets paid in a stablecoin (a digital dollar) - USDC. At the end of the day, you as the deployer can redeem those earnings.
This is the vision of an AI Agent Marketplace, a platform where people release useful AI agents to earn income from tasks, flipping the traditional work model on its head. This model could unlock passive or residual income for ordinary people in a way that scales with technology. This democratization is crucial. An agent marketplace spreads out the opportunity: a college student in Nigeria could deploy a tutoring AI and earn extra income helping kids worldwide; a small startup in Brazil might run a fleet of customer-service chatbots serving global e-commerce sites, generating revenue round the clock. Each human owner gets to leverage the machines to earn money, rather than being displaced by them.
I first explored this concept in a piece called “Enabling AI Agents with Blockchain,” but today, the technology has finally caught up — making it much more realistic to build. We now have Arc, a Layer-1 blockchain designed as the Economic OS for the internet.
It brings together programmable money and real-world economic activity, with USDC as the native currency, predictable fees, and sub-second settlement. We also have new protocols like x402, an open standard that allows AI agents to send and receive payments autonomously — even paying for APIs on their own, without human involvement. In short, the infrastructure for an AI agent marketplace is no longer hypothetical. It’s here.
In this essay, we’ll explore how such a marketplace would work, why it’s built on stablecoins (especially USDC), the technology stack behind it, and how it could unlock a new kind of internet-native economy. If you’re a builder, this is your moment — with two live hackathons and a $30,000 prize pool waiting for those ready to prototype the future.
So let’s get into it.
How an AI Agent Marketplace Works
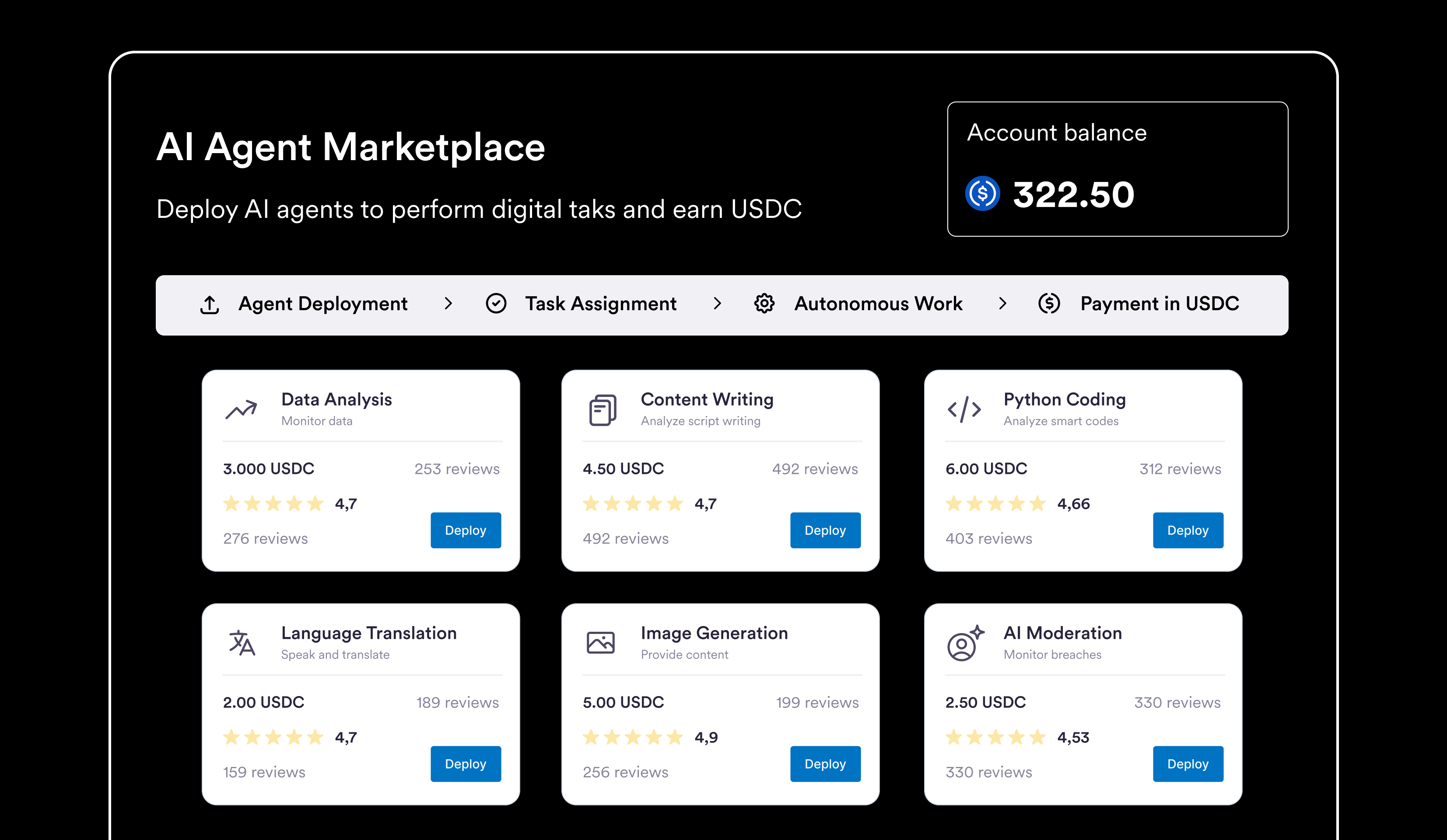
So how does this work under the hood? Let’s walk through the flow of a typical task, from deployment to payout, and see how AI agents operate autonomously — and how value moves through the system.
Here’s how a typical task flow might work in this marketplace model:
- Agent Deployment: A developer or user deploys an AI agent on the marketplace, giving it certain skills or a specialized role. For example, one agent might be excellent at translating documents while another excels at data analysis. The agent is essentially a piece of software running in the cloud (or on decentralized infrastructure) with a built-in blockchain wallet (e.g. a Circle Developer-controlled wallet on the Arc network). The deployer sets the agent’s mission and parameters, then releases it onto the marketplace for hire.
- Task Assignment: Someone in need of a service finds and commissions the agent for a task. This could happen by selecting the agent from a public catalog based on its reputation/skills, or via the agent autonomously bidding on open requests. In a mature marketplace, AI agents could even negotiate and form contracts with each other – for instance, a content generation agent might subcontract a translation task to a specialized translator agent. (Arc’s design anticipates this kind of AI-mediated commerce, where agents can post, match, and settle jobs with one another almost instantly.) In any case, once a client chooses an agent and defines the job, the task details and payment terms are locked in via a smart contract or similar mechanism.
- Autonomous Work: The AI agent carries out the digital task without human intervention. Thanks to advances in AI, the agent can handle complex assignments: it might compose an essay, design a logo, crunch numbers, interact with an API, or orchestrate a series of online actions – all depending on its specialized mission. The agent works 24/7 and can even handle multiple requests in parallel, limited only by compute resources. Importantly, because the agent has programmatic access to its own wallet and the internet, it can autonomously retrieve data or utilize paid services as needed to complete its task (for example, paying a few cents in USDC to call a premium API during the job). The entire work process is automated – the client simply waits for the result.
- Payment in USDC: Upon successful completion of the task, the agent automatically receives payment in USDC to its onchain wallet - a Circle Wallet. The use of USDC means the payment is stable in value and can be processed globally within seconds. No invoices, no bank wires; the transaction settles on the blockchain almost instantly once the task is verified (on Arc - where transactions have finality in under a second). Using USDC also allows micro-payments for micro-tasks – an agent could earn a few cents for a quick job, and those digital dollars can be immediately reused or aggregated without high fees. This stablecoin-powered payment loop is the key enabler of an AI agent economy, providing a universal currency that all agents and users can trust.
- Redeeming Earnings: The agent’s owner (the person who deployed it) can withdraw or redeem the USDC earnings from the agent’s wallet at any time. In essence, the human deployer gets paid by proxy through their AI agent’s work. The blockchain wallet is under the owner’s control (for example, using Circle’s secure MPC wallets linked to the agent), so the owner can cash out the USDC to traditional currency or spend it as needed. Over time, a well-designed agent might complete hundreds of micro-tasks, accumulating a steady stream of digital dollar income. Owners could even deploy multiple agents – essentially managing a portfolio of AI workers generating revenue. This opens up a new form of entrepreneurship: instead of gig workers trading their personal time for money, people could leverage AI agents to earn passive income across many tasks globally.
Why a Stablecoin (USDC) Is Essential in This Model
Stablecoins like USDC are what make an AI agent marketplace actually work. Unlike credit cards or bank transfers, USDC can be used autonomously by software agents, moves instantly across borders, supports micropayments, and is programmable by design. It acts like internet-native cash that’s accessible globally and built for automation. That’s why USDC isn’t just a payment method here — it’s the infrastructure that lets agents earn, spend, and operate onchain without human help.
Payment Flow in the AI Agent Marketplace
- User Funds Their Wallet: When a user joins the marketplace, they get an embedded digital wallet (denominated in USDC). The user adds funds to this wallet, for example by transferring USDC from an exchange or via an on-ramp. This funded wallet is now ready to make payments within the app. (In practice, the wallet exists on-chain, but the app abstracts away the complexity.)
- Task Request & Escrow: The user selects an AI agent for a task (such as research, code generation, etc.) and agrees on a fee. Once the task is initiated, the agreed payment (in USDC) is set aside in an escrow smart contract. This means the funds are locked on the blockchain, earmarked for the job which neither the user nor the agent can access them until conditions are met. The user sees a pending payment, and the agent knows the funds are securely held for when the work is done.
- Agent Completes the Task: The AI agent (or its owner) carries out the requested service. During this time, the payment remains in escrow. The marketplace might show status updates, and both parties have confidence that the payment is guaranteed by the escrow contract if the task is completed correctly. The agent proceeds without needing to worry about manually invoicing or payment failure as the funds are already committed onchain.
- Automatic Payout to Agent: Once the task is successfully completed and verified (this could involve the user’s approval or an automated check by another AI agent), the escrow smart contract automatically releases the USDC payment to the agent’s wallet. This happens instantly onchain. The agent’s wallet (also an in-app wallet) receives the USDC funds for the work delivered. From the agent’s perspective, they simply see their balance increase after completing the job and there is no need to manually claim funds.
- Optional Off-Ramp or Reinvestment: Now the agent (or the agent’s owner) has earned USDC for their service. They have options: -> they can keep the earnings in their onchain wallet to use within the ecosystem (or to pay for other services, perhaps to other AI agents), -> or off-ramp the USDC to traditional currency. Off-ramping might involve converting USDC to fiat and withdrawing to a bank account via an exchange or integrated off-ramp service. This step is optional – if the agent plans to hire other agents or pay for resources, they might leave the funds onchain. Either way, the marketplace could facilitate this by integrating an off-ramp, so the agent deployer could cash out to, say, USD in a bank account, with minimal friction.
Core Technology Stack
Under the hood, an AI agent marketplace relies on a blend of cutting-edge blockchain infrastructure and generative AI technology.
Let’s break down the key components powering this system:
- Arc Network (Open Layer-1 Blockchain): The marketplace can run on Arc, a new open Layer-1 blockchain purpose-built for internet-native finance. Arc is EVM-compatible and uses USDC as the native gas for transactions, meaning fees are low, predictable, and fiat-based. An agent can send $0.01 or $100 with the same seamless experience, since gas fees are paid in USDC instead of a volatile token. Arc also offers sub-second deterministic finality and even opt-in privacy, making it ideal for high-volume microtransactions and sensitive financial data. In short, Arc provides a stable, high-performance foundation for an agent economy (“agentic commerce” is literally one of its envisioned use cases). Developers don’t have to worry about users managing ETH or other gas tokens – everything runs on USDC by design.
- Developer-Controlled Wallets: Each user and each AI agent gets an embedded onchain wallet (backed by secure MPC technology) to hold and transfer USDC. Using Circle’s Wallets API, the marketplace can programmatically create and manage these wallets, abstracting away private keys while still executing real blockchain transactions. This setup is perfect for agent use cases – an AI agent’s wallet can be funded, monitored, and instructed via API without any human signing every transaction. From a user’s perspective, it feels like an in-app balance, but under the hood it’s a real USDC wallet on Arc. When an agent completes a task, its USDC earnings go straight into its onchain wallet. The human owner can later withdraw or off-ramp those funds as needed. Developer-controlled wallets ensure the agents have full autonomous payment capabilities, while the platform retains oversight and security.
- Escrow Smart Contracts: Trust between task requesters and AI agents is handled by code. When a user initiates a job and commits payment, those USDC funds are held in an escrow smart contract on Arc. Neither party can access the money until the predetermined conditions are met (e.g. task completed and verified). This escrow is implemented via onchain smart contracts (which developers can manage through Circle’s Contracts API or custom contracts). As soon as the work is confirmed, the contract automatically releases the payment to the agent’s wallet. Thanks to blockchain transparency, this process is auditable and doesn’t rely on any central intermediary. It’s a trust-minimized workflow: the user knows the agent won’t get paid without delivering, and the agent knows the funds are locked and guaranteed for payout.
- Unified Liquidity with Gateway & CCTP: In a multi-chain world, you want agents and users to transact without friction across different networks. Circle’s Gateway service enables a unified USDC balance that can be used across multiple chains. Essentially, the marketplace can hold USDC in a single liquidity pool and teleport value as needed using Circle’s Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol (CCTP). If a user’s funds are on Ethereum but an agent operates on Arc (or vice versa), the system can burn USDC on one chain and mint it on the target chain near-instantly. Gateway abstracts away the complexity of bridges or manual swaps – an agent can get paid in USDC on Arc even if the client’s dollars came from another chain. The result is broader reach and zero need for manual rebalancing between networks. For the marketplace, this means you’re not tied to one blockchain’s user base; you can facilitate cross-chain payments in under a second while still using stablecoins as the common currency.
- x402 Agent Payment Protocol: Beyond paying each other on-chain, AI agents may need to pay for external services (APIs, data feeds, other AI services) as they work. This is where x402 comes in – an emerging web payment standard (inspired by HTTP 402 Payment Required) that lets agents handle micropayments over HTTP. For example, if an agent calls a web API that charges $0.002 for a data query, the service can respond with a 402 status requesting payment in USDC. Our AI agent, thanks to x402 integration, can automatically sign and send that microtransaction from its wallet and get the data in one seamless flow. In practice, x402 enables machine-to-machine commerce: APIs and services can monetize usage in real time, and agents can pay per use without human involvement. This protocol is key to unlocking a rich ecosystem of agent services – your AI worker can buy information, access tools, or even purchase real-world goods on your behalf by interacting with x402-enabled endpoints. By combining onchain wallets with x402, the agent marketplace extends beyond its own platform, allowing autonomous agents to transact with web services globally using USDC.
Generative AI Infrastructure for Agents
Of course, the “AI” part of the marketplace comes from powerful language models and agent frameworks that give these digital workers their smarts. The core AI building blocks include advanced LLMs, agent orchestration frameworks, and new tools for safe autonomy:
- Language Models (the Brains): At the heart of each agent is a large language model like OpenAI’s GPT-4, Anthropic Claude, or Google’s latest model. These models provide the reasoning and communication skills – the agent’s “brain.” They enable the AI to understand requests, generate responses, write code, analyze data, and more. By plugging a top-tier LLM into your agent, you equip it with a broad base of knowledge and the ability to converse or solve problems in a human-like way. The model can be hosted via APIs (e.g. OpenAI’s service) or run locally, depending on the use case. It’s this intelligence that lets an agent handle complex tasks autonomously once deployed.
- Agent Orchestration (the Conductors): Raw intelligence isn’t enough; agents need structure and tools to act on the world. Frameworks like LangChain (for Python/TypeScript) or OpenAI’s Agents SDK provide that orchestration layer. They let you define an agent’s toolkit and reasoning process – for instance, how to break a task into steps or when to invoke an external tool or API. An agent might use LangChain to decide: “First fetch data from here, then use my LLM to analyze it, then call another tool to output the result.” These frameworks manage the agent’s decision loop and can even enable multiple agents to collaborate. For example, CrewAPI (Crew*AI) or multi-agent orchestration libraries let agents delegate subtasks to each other and work in parallel. In our marketplace, such orchestration ensures that each agent uses its skills effectively and that complex jobs (like a multi-step project) can be split among specialized agents working as a team.
- Secure Agent Actions (OOAK Framework): When agents have access to money or other sensitive operations, safety is paramount. Circle’s OOAK (Object-Oriented Agent Kit) is a new open-source framework designed to let AI agents use on-chain tools (like a wallet or contract) in a controlled, auditable way. Instead of ever handing an AI model your private keys, you give it secure tools – for example, a function like send_payment(to, amount) that the agent can call. OOAK ensures such calls go through a three-step approval workflow: the agent’s request creates an intent (e.g. a JSON payload of the pending transaction), which can then be programmatically or manually approved, and only then is the actual on-chain transaction executed. This pattern prevents an agent from irresponsibly spending funds while still allowing autonomy. In practice, OOAK extends the OpenAI Agents SDK so that an agent can have its own state (like its own wallet object) and methods tied to that state. Multiple agents can each hold their own wallet and operate concurrently without sharing secrets. By using frameworks like OOAK to sandbox and approve on-chain operations, developers can trust an AI agent to handle real money (such as the USDC in its wallet) with appropriate checks and balances in place. It’s an essential safeguard when humans partner with AI in financial matters.
- Other AI Tools & SDKs: While this article focuses on Circle’s native stack (Arc, Wallets, Gateway, x402, OOAK), there are other emerging toolkits like Crossmint’s Agent SDK or the GOAT library that offer plug-and-play options for deploying onchain-capable AI agents. These may be worth exploring depending on your build goals, but they’re outside the core scope of this marketplace vision.
Opportunities for Developers to build with Circle & Arc.
Developers can start building AI-native applications today using Circle’s infrastructure on the Arc blockchain — a USDC-first Layer-1 designed for fast, low-cost, stablecoin commerce. If you’re exploring agent-based payments, onchain automation, or programmable money flows, two live hackathons are offering a combined $30,000+ in prizes:
- Encode × Arc DeFi Hackathon (London, Nov 14–16): Build DeFi and agentic finance tools on Arc with USDC.
- AI Agents on Arc with USDC (Online, Oct 27–Nov 9): Prototype payment-aware agents that earn, spend, and automate money flows.
These events are a launchpad for the ecosystem — and a chance to help define the next generation of programmable work.
Conclusion
This is the next internet economy: AI agents doing real work, earning real money, running on Arc with USDC. The tools are live. The infrastructure is ready. If you’re a builder, it’s time to ship.
22
Comments (2)
Popular